[ad_1]
The world’s largest iceberg, A23a, is drifting towards South Georgia Island, a distant and ecologically important wildlife haven.
This large block of ice, concerning the dimension of Rhode Island, poses a major risk to the fragile ecosystem of the island, dwelling to penguins and seals.
Satellite tv for pc pictures, together with latest knowledge captured by NOAA’s GOES East satellite tv for pc on Jan. 22, 2025, are carefully monitoring the iceberg’s sluggish journey by way of the Southern Ocean, the place it may quickly attain the shallow waters surrounding South Georgia.
Breaking free
Iceberg A23a has been a priority for scientists because it broke away from the Antarctic ice shelf in 1986. After remaining motionless for over three a long time, the iceberg lastly broke free in 2020 and commenced drifting northward.
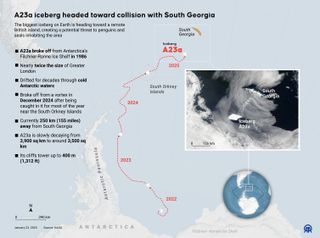
Measuring roughly 1,350 sq. miles (3,500 sq. kilometers) throughout, A23a is the world’s largest and oldest iceberg in keeping with AFP Information. Its imposing dimension and sluggish, regular motion have captivated oceanographers and researchers alike, although predicting its precise path has confirmed tough because of the unpredictable forces of ocean currents.
Not like many earlier “megabergs” that crumble into smaller chunks, A23a has proven little signal of breaking up, which has solely intensified issues over its collision with South Georgia Island.
Based on Andrew Meijers, a bodily oceanographer on the British Antarctic Survey, the iceberg is presently shifting northeastward, however prevailing currents counsel that it may strike the shallow continental shelf round South Georgia in two to 4 weeks. If it does, the implications may very well be dire for the island’s wildlife Meijers advised AFP Information.

Potential impression
The potential impression on South Georgia Island’s ecosystem is worrying. Penguins, seals, and different marine animals rely upon the island’s surrounding waters for meals and breeding. If A23a grounds itself on the continental shelf or disrupts the currents, it may block entry to important feeding areas.
Meijers warned that icebergs have beforehand grounded close to the island, inflicting important mortality amongst penguin chicks and seal pups, notably when their feeding grounds have been minimize off by the ice. Such a situation may hinder the survival of those already susceptible species, particularly throughout the essential breeding season.

Hit and miss?
Regardless of these issues, there’s nonetheless a level of uncertainty surrounding the iceberg’s path. It is attainable that A23a may keep away from the shelf and drift into open water, bypassing South Georgia altogether.
Alternatively, the iceberg may turn into caught for months or break aside into smaller items, each of which may severely impede seals and penguins making an attempt to feed and lift younger on the island, in keeping with Meijers.
Raul Cordero from Chile’s College of Santiago and a part of the Nationwide Antarctic Analysis Committee stated he was assured the iceberg wouldn’t impression South Georgia.
“The island acts as an impediment for ocean currents and due to this fact often diverts the water lengthy earlier than it reaches the island,” Cordero advised AFP Information.

“The iceberg is moved by that water move, so the probabilities of it hitting aren’t that prime,” although chunks may, Cordero stated.
Glaciologist Soledad Tiranti, who’s presently a part of an Argentinian exploration mission in Antarctica, defined that icebergs like A23a are so large that they usually turn into grounded on the seabed earlier than reaching an island or the mainland, in keeping with AFP Information.
The state of affairs stays fluid, and scientists are maintaining an in depth eye on the iceberg’s progress with common satellite tv for pc imagery and ocean monitoring.
[ad_2]
